Etude de la XR dans l'Education
Les technologies de Réalité Spatiale (RS) révolutionnent l’éducation en offrant des environnements immersifs et interactifs qui relient les mondes physique et numérique. Une étude récente de l’Université Nationale de Singapour (NUS) met en avant des applications innovantes de la RS dans l’enseignement de la chimie, avec plus de 87,5 % des étudiants ayant jugé la formation en réalité virtuelle très efficace lors des essais. Ces résultats soulignent le potentiel de la RS pour améliorer les résultats d’apprentissage dans diverses disciplines.
Qu'est-ce que la Réalité Spatiale?
La Réalité Spatiale « Spatial Reality » englobe la Réalité Virtuelle (VR), la Réalité Augmentée (AR) et les technologies de réalité étendue, permettant aux utilisateurs d’interagir de manière fluide entre les environnements physiques et digitaux. En intégrant ces outils, les enseignants créent des expériences d’apprentissage dynamiques qui favorisent la rétention des connaissances et l’engagement des étudiants.
Les bénéfices du Spatial Learning dans l'Education
Les études montrent que les technologies de Réalité Virtuelle améliore l’efficacité des cours, en particulier dans les contextes axés sur l’action et la résolution de problèmes :
- Amélioration de la rétention des connaissances : Des méta-analyses indiquent que la VR immersive est plus efficace que les méthodes traditionnelles, notamment dans l’enseignement des sciences.
- Engagement des étudiants : Lors d’essais menés à la NUS, 64 % des étudiants ont rapporté une expérience positive, mettant en évidence le pouvoir motivationnel de la VR
Surmonter l'anxiété d'enseigner en VR
Un obstacle majeur à l’adoption de la Réalité Spatiale (RS) est l’« anxiété de l’enseignement en VR », qui découle des préoccupations liées à la maîtrise technique et au manque de soutien institutionnel. Pour y remédier, il est essentiel de :
- Développer les compétences professionnelles : Former les enseignants à l’utilisation efficace des outils de RS.
- Simplifier les outils : Des plateformes comme Uptale, ne nécessitant aucun codage, rendent la RS accessible aux enseignants ayant une expertise technique limitée.

Les cas d'usages de l’Université Nationale de Singapour (NUS)
NUS a démontré des applications innovantes et utiles de la Réalité Virtuelle dans l’éducation :
Chimie en VR
Enseignement des techniques d’échantillonnage environnemental à travers des expériences immersives
Laboratoire Métavers
Un laboratoire virtuel immersif en VR, où les étudiants peuvent comprendre des protocoles tels que la gestion des déversements chimiques et les interventions d’urgence, dans un environnement sans risque.
Scènes de crime en VR
Pratique des sciences forensiques dans des scènes de crime virtuelles, avec 79 % des étudiants exprimant un retour positif.
Ils ont reproduit une véritable scène de crime avec tous les indices, l'ont filmée et l'ont intégrée à Uptale.
Excursions virtuelles
Exploration de sites internationaux et de concepts environnementaux sans contraintes logistiques.
Métavers et Éducation : Un Laboratoire de Chimie Virtuel
L’étude présente également MyVirtualLab, une plateforme inspirée du métavers développée à la NUS pour enseigner la sécurité en laboratoire et les techniques expérimentales (comme la gestion des déversements chimiques et les interventions d’urgence). Conçu pour les étudiants en chimie, cet outil permet des interactions multi-utilisateurs et offre un environnement immersif et sans risque pour l’apprentissage pratique, grâce à l’Oculus Quest 3.
Une étude menée auprès de 16 étudiants en Master of Science en Chimie Industrielle a évalué l’efficacité de MyVirtualLab pour la formation à la sécurité en laboratoire. Les résultats ont montré une amélioration de 14 % des connaissances en sécurité, soulignant ainsi son efficacité.

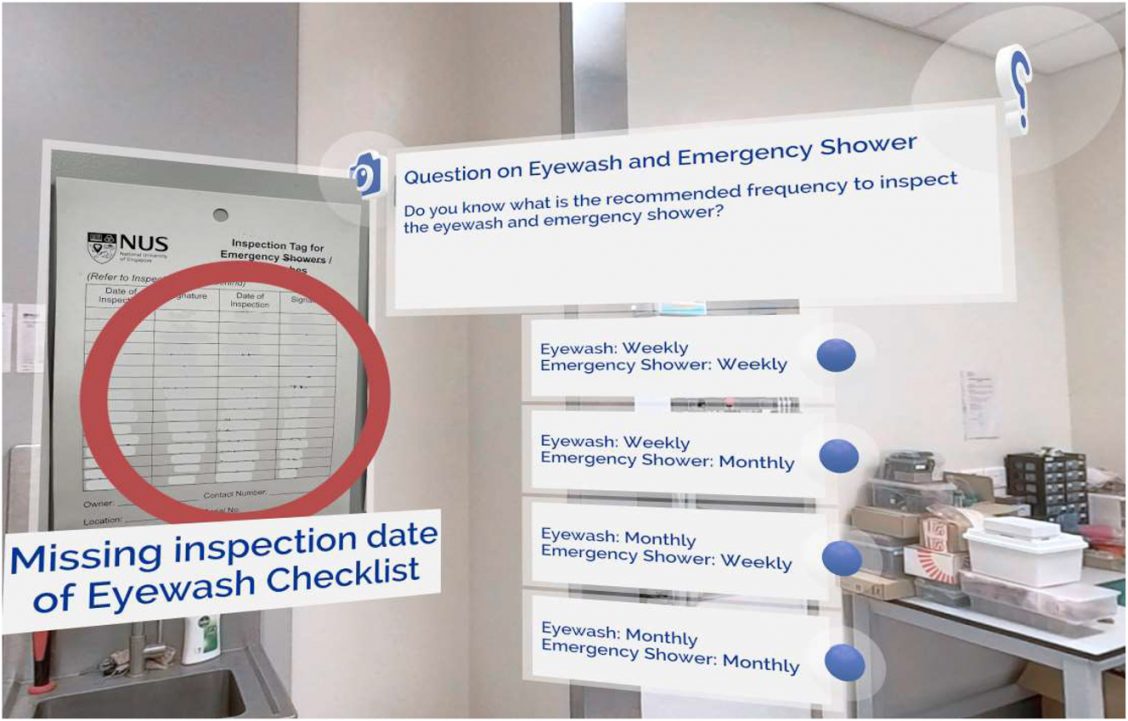
Des vidéos 360 pour former à l'Inspection des laboratoires
Au-delà de MyVirtualLab, la formation en inspection de laboratoire en VR, développée avec Uptale, a démontré une efficacité éducative similaire :
- Formation standardisée : Permet aux stagiaires d’identifier systématiquement les dangers dans différents environnements de laboratoire.
- Engagement des utilisateurs : 87,5 % des participants ont jugé la formation efficace, et beaucoup l’ont recommandée à d’autres.
- Sensibilisation accrue aux dangers : Des fonctionnalités interactives, comme des quiz, des cartes thermiques pour repérer les dangers manqués et des tâches de relocalisation d’objets (ex. : rangement correct des produits chimiques), ont amélioré la détection des risques et les compétences pratiques.
Recommandations pour les Enseignants
Pour exploiter pleinement le potentiel de la Réalité Virtuelle, l’étude recommande de :
- Contextualiser le contenu avec des applications concrètes du monde réel.
- Collaborer avec les étudiants pour concevoir des expériences immersives et impactantes.
- Faire appel à des professionnels de la VR pour développer des projets éducatifs avancés.
Ces approches permettent non seulement d’améliorer l’engagement des étudiants, mais aussi de réduire l’appréhension des enseignants face à ces technologies.
Conclusion
L’Université Nationale de Singapour est à l’avant-garde de l’intégration de la Réalité Spatiale dans l’éducation, montrant ainsi sa capacité à transformer les méthodes d’apprentissage traditionnelles.
Avec des données éclairantes indiquant un meilleur engagement des étudiants et une rétention des connaissances améliorée, les technologies XR offrent un avenir prometteur pour une éducation innovante et efficace.




